研究の目的
昆虫が特異的にもつ先天的免疫に着目し、抗微生物タンパク質の特性と発現機構を明らかにするとともに、優れた抗菌活性を示すペプチドを改変しその機能を強化することにより、畜産分野における薬剤耐性病原細菌の制御等感染症対策上の新たな基盤技術の可能性を探る。
研究項目及び実施体制(◎は研究代表者)
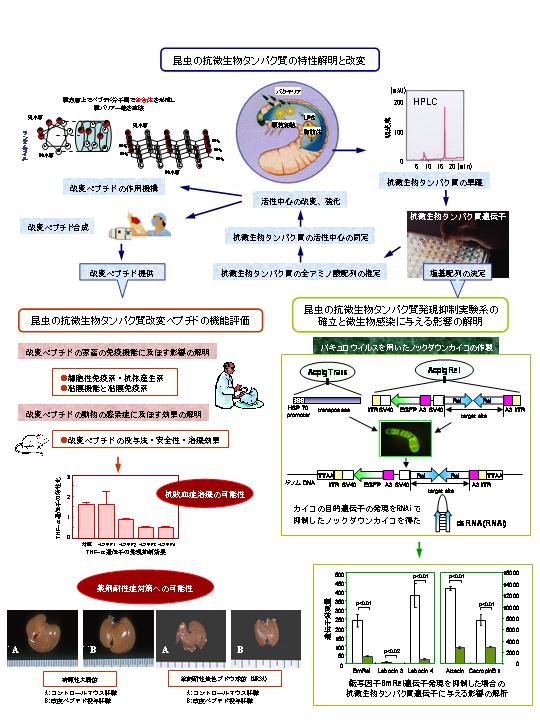
- 昆虫の抗微生物タンパク質の特性解明と改変
(◎山川 稔/(独)農業生物資源研究所) - 昆虫の抗微生物タンパク質発現抑制実験系の確立と微生物感染に与える影響の解明
(森 肇/京都工芸繊維大学繊維学部) - 昆虫の抗微生物タンパク質改変ペプチドの機能評価
(中村 菊保(16年度まで廣田 好和)/(独)農業・生物系特定産業技術研究機構動物衛生研究所)
研究の内容及び主要成果
- 種々の昆虫の抗微生物ペプチドの構造や性質、遺伝子発現様式を明らかにした。これを基に活性中心を改変し抗菌機能を強化した改変ペプチドを多数作成し、各種の細菌に対する作用特性を解析するとともに、これらが細菌細胞膜の膜バリアー能を物理化学的に直接破壊する抗菌メカニズムを明らかにした。
- 鱗翅目昆虫では世界初で、かつ、簡易、高効率の遺伝子発現抑制形質転換カイコの作出技術を開発した。このRNAi 技術を利用して細胞内シグナル伝達に関与する転写因子の一つであるRel のわずかな構造差によって抗微生物タンパク質遺伝子の選択的活性化が引き起こされるという新しい現象を明らかにした。
- マウス生体を用いて各種改変ペプチドの抗菌機能を評価し、その中からメチシリン耐性黄色ブドウ球菌や病原性大腸菌による感染阻止に有望なものを得た。またエンドトキシンショックモデルマウスを用いて、改変ペプチドがTNF- α遺伝子の発現を抑制することによって治癒効果を示すことを明らかにした。
見込まれる波及効果
畜産分野における新しい薬剤耐性病原細菌による感染症の治療剤や外用薬としての抗細菌剤等の利用が期待される。
主な発表論文
- Hemmi H., et al.: Structural basis for new pattern of conserved amino acid residues related to chitin-binding in the antifungal peptide from the coconut beetle, Oryctes rhinoceros. J. Biol. Chem. 278 : 22820-22827 (2003)
- Saido-Sakanaka H. et al.: In vitro and in vivo activity of antimicrobial peptides synthesized based on the insect defensin. Peptides 25: 19-27 (2004)
- Sakurai T., et al.: The sex pheromone receptor in the silk moth, Bombyx mori. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 101 : 16653-16658 (2004)
- Yamamoto M. et al. A new and highly efficient method for the silkworm transgenesis using Autographa californica nucleopolyhedrovirus and piggyBac transposable elements. Biothechnol. Bioeng. 88 : 849-853 (2004)
- Yamada M., et al.: Therapeutic effect of modified oligopeptides from the beetle, Allomyrina dichotoma on methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) infection in mice. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 67 : 1005-1011 (2005)
- Koyama Y., et al.: Protective effects of antimicrobial peptides derived from the beetle, Allomyrina dichotomadefensin on endotoxic shock in mice. International Immunopharmacol. 6 : 234-240 (2006)
研究のイメージ