Overview
Recently, the land is experiencing unusually heavy rain events and resulting flood damages in various areas. Moreover, the risk of disaster is expected to grow due to the influence of the climate change and other reasons.
In addition to the large-scale investment to infrastructure such as dam construction, the active engagement to "paddy field dam" project to mitigate the flood damage is one of the countermeasures that local farmers and communities can take. Paddy fields have an innate flood mitigation function to store rain waters and to drain them gradually afterwards rather than discharging them all at once. The concept of the "paddy field dam" is to reinforce this function and maximizing its capacity of storing rainfalls, by installing the runoff control devices at the drainage boxes of the plot to control the water level inside. The initial engagement to promote "paddy field dam" had started in Niigata prefecture and has been spreading to other parts of the country.
The National Agriculture and Food Research Organization (NARO) has developed a reference showing the acceptable ponding water depth and the ponding duration in each growth stage of rice to grow without decreasing its yield. It is shown that even when the rice plants are in the water stored in the paddy field, there won't be a negative impact on its yield if the depth and the duration are within the range shown in the reference, and such an information showing the relationship between the submergence degree of the plant and its yield wasn't available up to the present. It is expected to foster better understanding among the paddy field owners, which is an essential premise for their cooperation to increase the "paddy field dam" engagement. The project also includes the development of the runoff control devices to control the ponding water level inside the paddy field. The "Dam keeper" is a rectangular weir plate with a slit, and the "Field gate" is a device with an orifice, to be set together at the drainage boxes of a paddy field plot. They regulate the outflow from the paddy field and therefore control the ponding water level inside.
The release of the reference and the developed devices are expected to contribute to the further spread of "paddy field dam" and result in the mitigation of flood damages after heavy rainfalls.
For Inquiries
Contact: http://www.naro.affrc.go.jp/english/inquiry/index.html
Reference Information
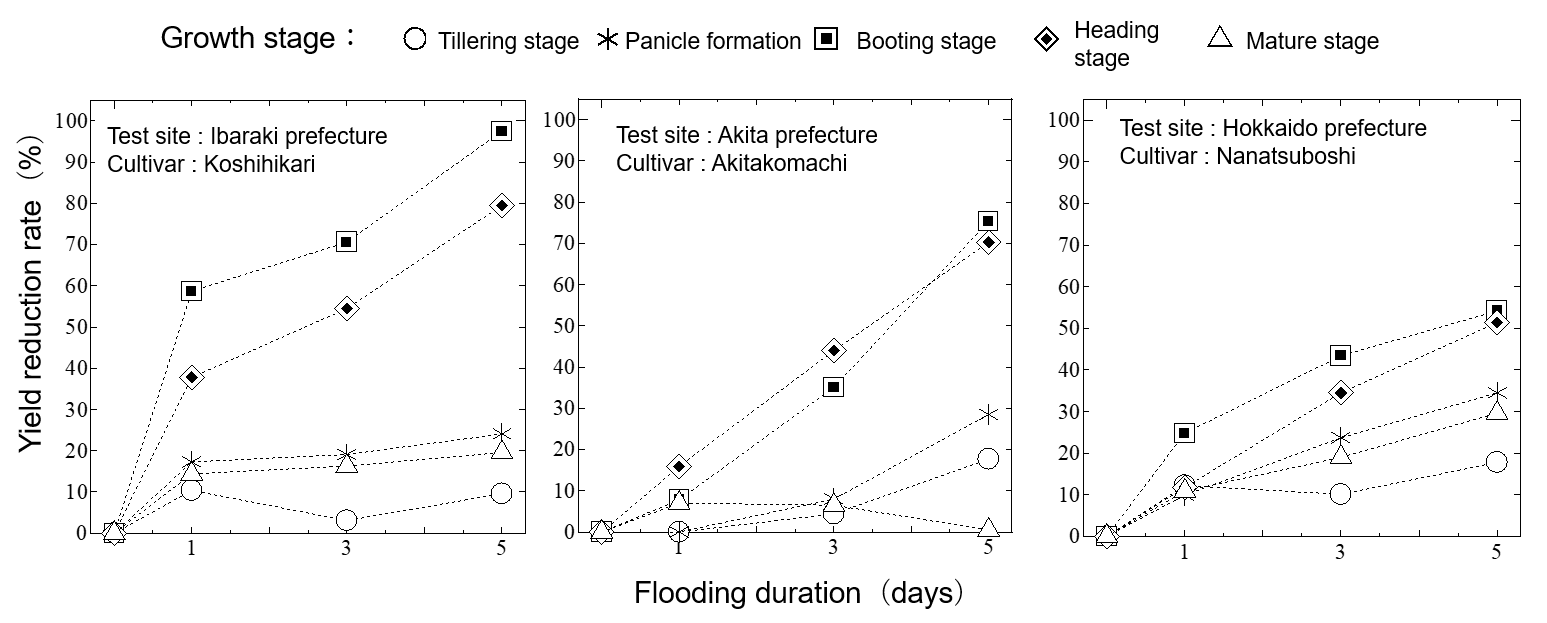
Fig.1 Examples of the relationship between flooding duration and yield reduction among different cultivars
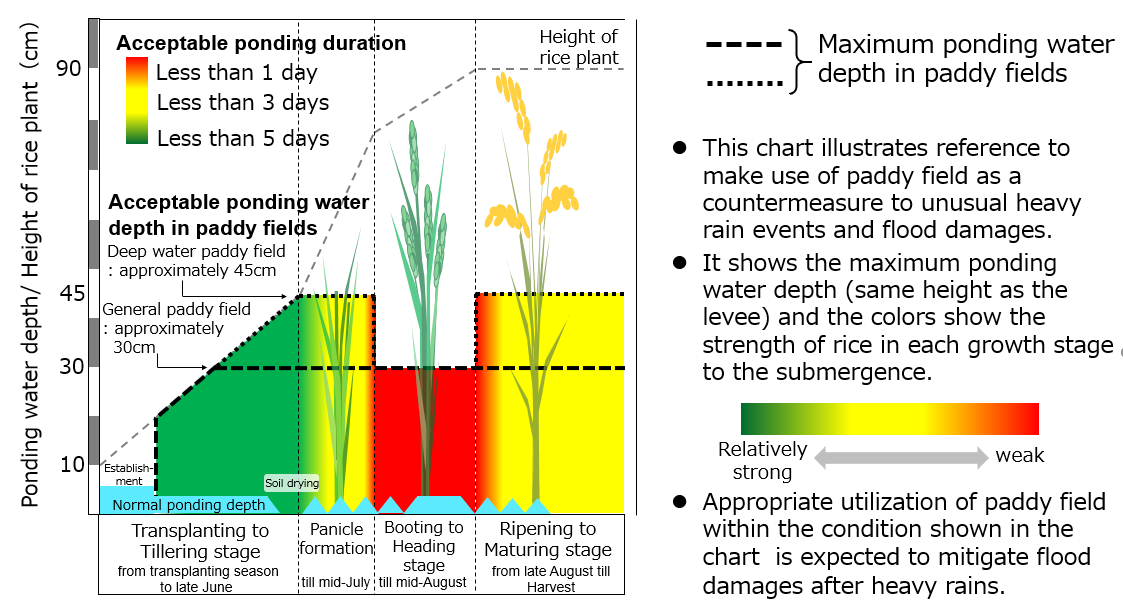
Fig.2 Example of the acceptable ponding water management according to the relationship between ponding duration and yield reduction
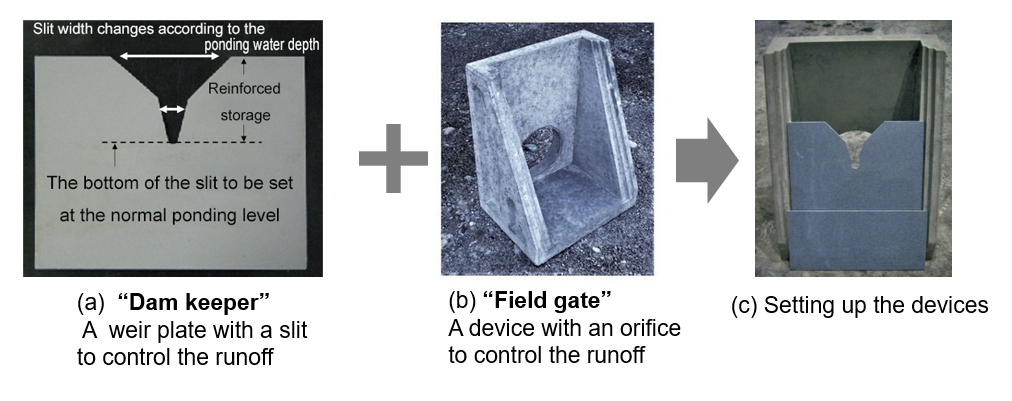
Fig.3 Devices developed in our project to make use of paddy fields as "paddy field dam"
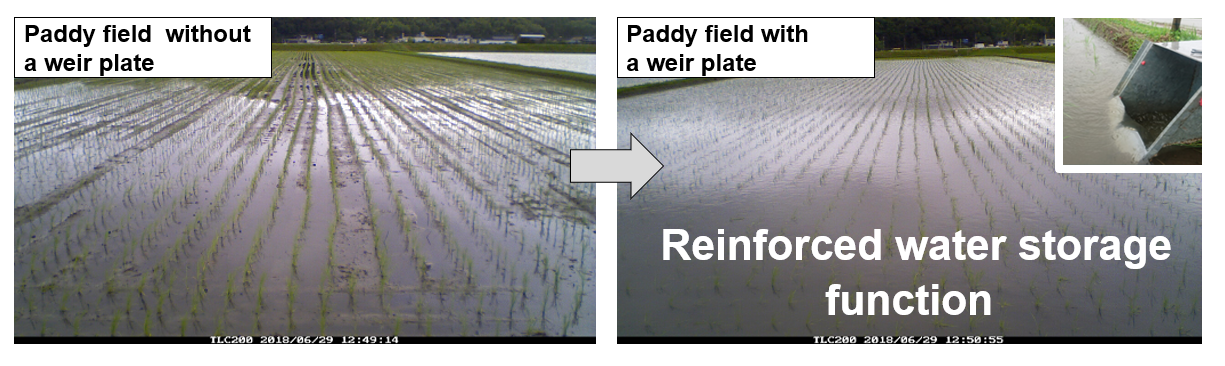
Fig.4 The "paddy field dam" effect seen in actual paddy fields
(Observed from June 28th to July 1st, 2018)
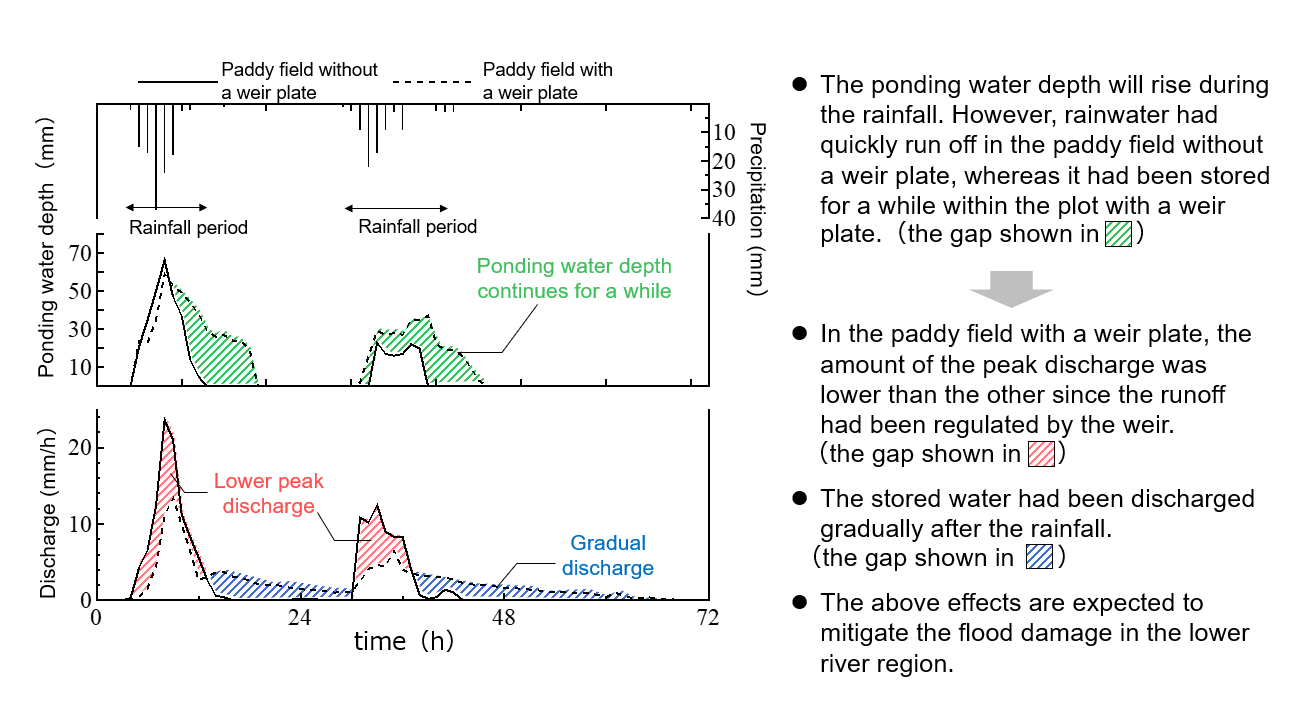
Fig.5 The "paddy field dam" effect shown in a chart
(Observed from June 28th to July 1st, 2018)




