The Institute for Rural Engineering, NARO (NIRE) has developed a water management control system that efficiently distributes water based on its usage by linking the pumping stations controlled by the land improvement district and the automatic hydrants in farms managed by farmers using ICT. The Irrigation and Drainage Automation System (iDAS) is expected to contribute in labor saving for facility managers in paddy field irrigation areas, saving in use of agricultural water, and saving in energy consumption of pumps.
Overview
The Institute for Rural Engineering, NARO (NIRE) has developed iDAS (Irrigation and Drainage Automation System), a water distribution management control system that controls the supply of agricultural water in pipelines using personal computers, tablets, or smartphones.
Currently, efforts to save labor in field water management by installing automatic water hydrant using ICT, IoT etc. are progressing. However, water facilities such as pumping stations managed by the land improvement districts are still managed manually. Hence, improvement and efficient automation of water management are necessary from the viewpoint of labor management, water and energy saving. The developed iDAS can automatically perform efficient water distribution in accordance with the water usage in the field, and is thereby expected to contribute in labor saving for facility managers in paddy field irrigation areas, saving in use of agricultural water, and saving in energy consumption of pumps. Moreover, planned irrigation management along with labor-saving for farmers by grasping the water usage can be achieved by coordinating the system with an automatic hydrant which was developed separately.
In the demonstration test, installation of this system reduced the power consumption of the pump station by 40% in the lowland paddy field pipeline irrigation area. In addition, since water is distributed while properly maintaining pipeline pressure, the pressure inside the pipe has drastically decreased which can extend the lifespan of the pipeline. Demonstration tests are still ongoing in different areas under various conditions.
The developed system is expected to be introduced in the land improvement projects of state-owned companies, prefectural companies and corporations, targeting the land improvement districts which manage agricultural irrigation facilities such as pump stations.
For inquiries
Contact: http://www.naro.go.jp/english/inquiry/index.html
Reference information
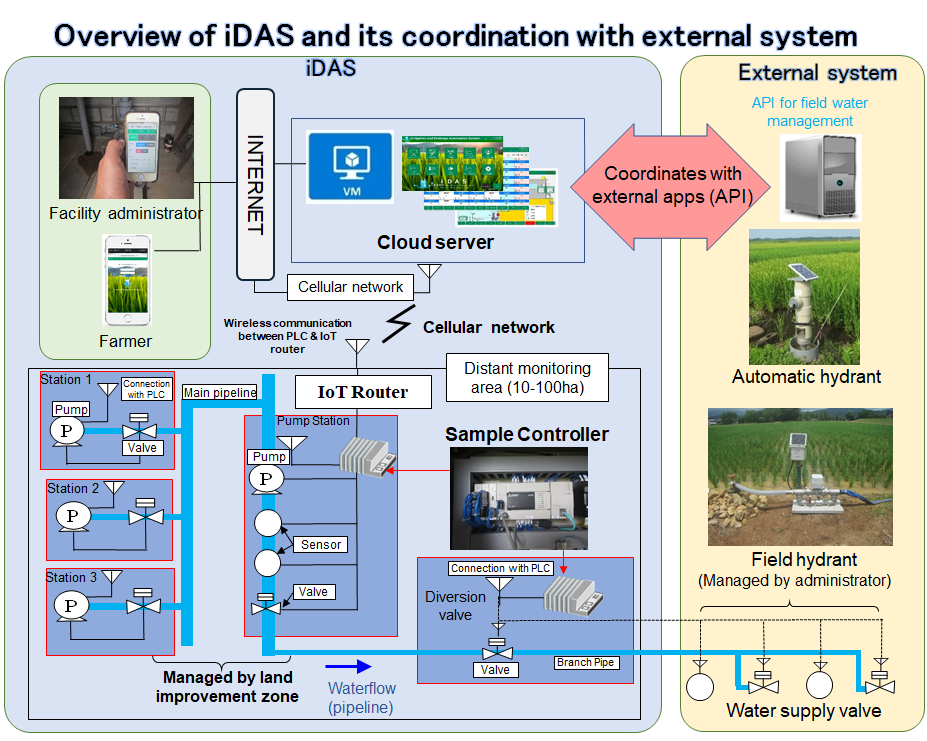
Fig.1: Overview of iDAS system
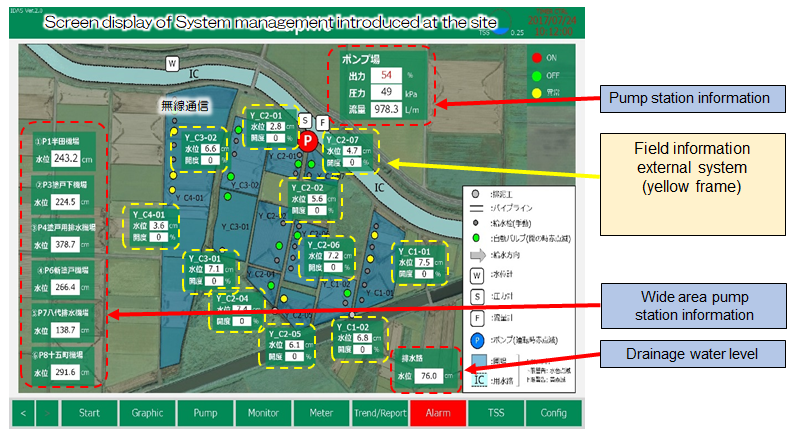
Fig. 2: Screen display of on-site system management (Ryugasaki, Ibaraki Pref.)
The iDAS can be installed and monitored in the water source of pumping station (red frame). Since it is coordinated with the installed field water management system (yellow frame), the paddy fields can also be monitored at the same time.

Fig. 3: On-site verification test (left) and pump station (right)
(Paddy field pipeline irrigation area in Ryugasaki, Ibaraki Pref.)

Fig. 4: Automatic water hydrant (left) and pump station control room (right)
(Paddy field pipeline irrigation area in Ryugasaki, Ibaraki Pref.)

Fig. 5: Monitoring and control of various terminals
Connection and control of pumps by smartphone (for personnel, facility managers (left))
Management by personal computer (for land improvement district (right))




