
The National Agriculture and Food Research Organozation (NARO, President: KYUMA Kazuo) and Nisshin Seifun Group (President: TAKIHARA Kenji) have discovered that alkylresorcinols in wheat bran have immune-enhancing properties. The health benefits of wheat bran consumption have been recognized recently. This research highlights, for the first time, that alkylresorcinols in wheat bran may directly upregulate the immune system. Read more
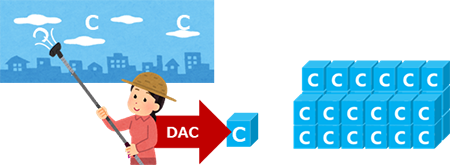
Crop forage such as rice straw is susceptible to rot and deterioration. Hence utilizing them in low-carbon and decarbonization industries that assume long-term carbon storage was challenging. The National Agriculture and Food Research Organization (NARO) has developed a new technology, the GrAAS process, which makes it easier to unravel the fibers of forage by treating them with acid at room temperature. A detailed analysis of this phenomenon was conducted in collaboration with Saitama University and the University of Tokyo. Read more

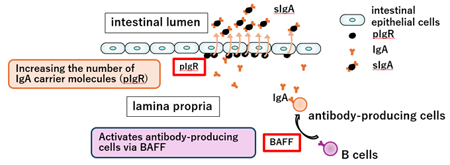
Foods with Function Claims can be labeled with function claims based on scientific evidence in Japan. The scientific evidence must be explained by one of the following methods: clinical trial with a finished product; or a systematic literature review on a finished product or functional substance. We conducted systematic literature reviews on functional substances. Read more

National Agriculture and Food Research Organization (NARO) has found that it is possible to create crunchy paste-like food by using cabbage core that have been dried and pulverized to adjust the size of the grains and has confirmed the conditions under which it can be created using a 3D food printer. By this not only we can take in the nutrients and functional ingredients of the cabbage core, which is a discarded part, but also by utilizing the firmness as a new means of expression of texture, we can expect to reduce food loss that occurs when producing cut vegetables. Read more

The National Agriculture and Food Research Organization(NARO) has developed the starch-based asphalt modifier C-AG. C-AG disperses fibrously in asphalt, improves the flow resistance of asphalt and helps in prolonging the road life. By means of using this newly developed asphalt modifier, energy consumption related to modified asphalt production and road construction is lower when compared to conventional asphalt modifiers, and Greenhouse gas(GHG) emissions can be expected to be reduced. Read more
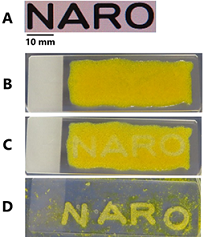
National Agriculture and Food Research Organization (NARO) has developed a new food material (Nata puree) by blending and crushing nata de coco and (1-3) (1-4) -β-glucan contained in barley. Nata puree adds new physical properties and processing properties to powders derived from agricultural products and improves the binding capacity and dispersibility of paste foods. This technology expands the scope of application of unused resources such as surplus and non-standard agricultural products to 3D printed foods, etc., and contributes to the reduction of food loss. Read more
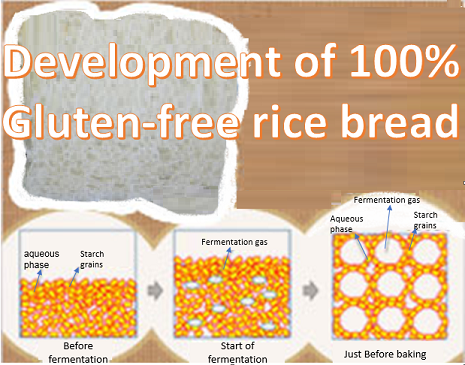
The Institute of Food Research, NARO (NFRI) in collaboration with Hiroshima University has developed a technology to manufacture 100% gluten-free rice read from basic ingredients such as rice flour, water, dry yeast, sugar, salt and butter, without using any additives or special equipment. The use of rice flour with less starch damage and devising the fermentation and baking processes facilitated bead-making with a specific volume of 4 mL/g or more which is comparable in consistency and volume to traditional wheat bread. This 100% gluten-free rice bread is suitable to people with wheat allergy or celiac disease, and is also expected to contribute in expanding domestic rice consumption. Read more. Press release link